The ability to measure and understand marketing performance has never been more critical. Effectively implementing your marketing measurement to get the most valuable data can make or break your marketing success.
So, what is marketing measurement, exactly? How do you collect and interpret your data? And which metrics do you need to track?
Today, we’re covering everything you need to know about marketing measurement, the key metrics and KPIs to use, and how to use your data to guide your campaigns and best allocate your resources to get the most out of your budget.
Let’s get right into it!
Understanding basic performance marketing principles, and the latest trends in marketing analytics, including the transformative impact of artificial intelligence and predictive analytics, is crucial for businesses to stay competitive.
Marketing measurement refers to how we track and measure the impact of our various marketing activities and campaigns.
By tracking the right metrics and using the appropriate KPIs, we can see where and how our marketing is driving meaningful action, that supports our business and marketing objectives.
It also allows you to see where your activities are not working optimally, and which activities need to be adjusted or abandoned in favor of activities that generate a better ROI for your marketing.
Let’s take a look at why marketing measurement is becoming more and more important for success:
In the face of a looming recession, marketing budgets are under increased scrutiny, making effective measurement and data utilization more vital than ever.
The trend towards Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) is growing, with businesses needing accurate forecasts to determine the minimum marketing budget necessary for survival.
This strategy necessitates a more in-depth understanding of the incremental impact of marketing and a mixed-measured approach that goes beyond standard attribution models.
As marketers, we have to be able to demonstrate the value and impact of our marketing, which is often challenging because there are so many moving parts, to justify the budget allocated to us.
Another critical aspect of marketing measurement is selecting the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for each campaign’s purpose.
In this era of data abundance, businesses should focus on leveraging the insights behind the data rather than merely collecting it. This makes it essential to collect the right data that will provide the insights you need.
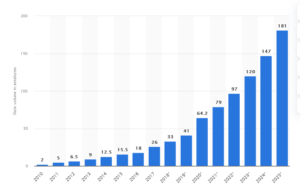
By 2025, it is estimated that 181 zettabytes of data will be collected and stored; that’s a 14.5-fold increase in a decade, and it’s growing exponentially.
This emphasizes the need for businesses to derive real value from these data points through insightful analysis rather than just data accumulation.
Likewise, in marketing, it is critically important to identify the data that’s actually useful, from the get go.
Furthermore, predictive analytics and forecasting are becoming indispensable tools for data-driven marketing decisions.
By employing accessible data, organizations can improve their understanding of their client’s requirements, seize new prospects, and quickly modify strategies.
This approach ensures customer satisfaction and drives sales, highlighting the growing need for businesses to adapt proactively to changing customer behaviors and preferences.
Additionally, the complexities of multi-channel attribution are increasingly significant, especially for B2B marketers.
This method entails crediting multiple marketing touchpoints across various platforms that lead to conversions.
As such, multi-channel attribution allows marketers to acquire a thorough picture of the influence of each touchpoint on the customer journey, allowing them to identify the most successful channels for generating sales and allocating resources more strategically.
In line with these trends, video marketing analytics are gaining prominence. With the increasing popularity and importance of video marketing, businesses are leveraging data-driven insights to optimize video content and measure its effectiveness.
Advanced measurement techniques are being adopted to gain deeper insights into audience engagement.
These include various metrics like analyzing viewer count, engagement levels, and viewer behavior. Each of these is critical for understanding the performance of a video marketing campaign.
Why Is Measurement Crucial?
The importance of marketing measurement lies in its ability to give businesses a deeper understanding of their marketing efforts. When adopting a mixed measurement approach, companies should focus on predictive analytics, multi-channel attribution, and video marketing analytics. As such, businesses can make informed decisions, adapt to changing market dynamics, and ensure the effectiveness of their marketing strategies.
As digital marketing continues to evolve, the significance of measuring its impact becomes increasingly important.
The types of marketing measurement methods are as varied as the campaigns themselves. Your marketing measurement framework is key to understanding and navigating this dynamic landscape.
Let’s take a look at the most important types of marketing measurement:
CPL, defined as the gross marketing cost spent to acquire a lead, is a key metric to track as it provides insight into the investment made to generate potential customer interest.
This metric is calculated by dividing the total marketing spend by the number of new leads acquired, and its importance lies in the quality of leads it represents.
For example, some channels may provide warm leads who are more likely to convert, while others might result in cold leads with a lower conversion rate.
Thus, tracking and measuring each lead generation channel is essential to optimizing marketing spend.
On the other hand, CPA provides a clear picture of the average cost of gaining one new customer.
Unlike CPL, CPA considers the complete journey of a lead to a paying customer, offering valuable insights into the marketing budget’s performance and potential profitability.
The CPA will vary depending on factors such as the nature of the products or services and the average order value.
For instance, selling high-end products might result in a higher CPA than more affordable items.
Calculating CPA involves dividing the variable marketing cost by the number of new customers acquired during a specific period, which helps fine-tune marketing strategies and budget allocation.
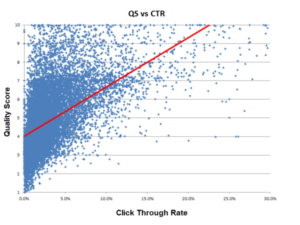
CTR is an essential indicator of the effectiveness of online advertisements or email campaigns.
It measures the frequency of clicks on a link, ad, or website relative to the number of impressions it receives.
This metric is crucial for gauging how well content captures and retains audience attention.
For example, average CTRs in 2023 were reported at 1.6% for Google Ads, with organic search positions showing significantly higher rates (39.6% for the first position).
Improving CTRs involves several strategies, such as crafting more customized meta titles and descriptions and addressing search intent to improve engagement rates.
Thought leadership-based SEO, which emphasizes high-quality content and responds to the audience’s search intent, is particularly effective in this regard.
Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) is a critical metric in assessing the long-term value of a customer to a business. It represents the gross margin a customer generates over their lifetime with a brand.
This metric is crucial for understanding customer retention and purchase frequency, although it does not directly indicate net profitability.
To calculate LTV, businesses should consider a specific time period, such as 6, 12, 24, or 36 months, which will depend on factors like purchase frequency and seasonality.
Visualizing CLV through graphs is beneficial, showing how the value changes over time, with an upward trend being desirable.
Length of engagement and bounce rate are essential website engagement metrics, providing insights into how visitors interact with a website and online brand.
These metrics can inform businesses about visitor behavior on the website, such as which pages they visit, how long they stay, and how often they return.
This metric, including average time on page and session duration, offers an understanding of how engaging and effective the website’s content is.
The longer visitors spend on a page or per session, the more engaging and valuable the content is considered. It is a strong indicator of the quality of visitors and the effectiveness of the website’s content strategy.
Bounce rate measures the percentage of visitors who leave a website after viewing only one page.
A high bounce rate might indicate issues with the website’s content, layout, or user experience, suggesting areas for improvement to retain visitor engagement.
Conversion rate by channel is a key metric for determining the effectiveness of different marketing channels in driving sales and conversions.
This metric helps businesses understand the impact of each marketing channel on their overall strategy and enables them to allocate resources more strategically.
By analyzing the conversion rates of various channels, businesses can identify which channels are most effective at converting visitors into leads or customers.
This insight is crucial for optimizing marketing strategies and maximizing return on investment.
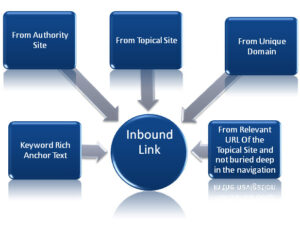
The quality of inbound links, or backlinks, remains a vital component of search engine optimization (SEO).
Inbound links from reputable sources such as industry publications, business associations, and suppliers are highly valued by search engines.
These links are crucial for enhancing Google’s trust in a site’s ability to provide relevant information to visitors.
Google uses backlinks from prominent websites as a signal to determine the quality and trustworthiness of content.
However, the importance of backlinks as a ranking factor has been evolving. While still significant, they are just one aspect of the broader context that constitutes a site’s authority.
In current SEO practices, focusing solely on link building is not sufficient. Google now evaluates a site’s authority based on various factors, including content ratings for expertise, experience, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness.
To stay competitive in the search landscape, it’s important to focus on updating these aspects of your site alongside securing high-quality backlinks.
Social media engagement metrics are crucial indicators of how well a social media strategy is performing.
These metrics act as scorecards for online posts and interactions, revealing how many people saw, liked, shared, or commented on a content item.
They provide insights into the return on investment (ROI) of social media efforts and are essential for aligning social media activities with real business goals.
Engagement metrics demonstrate the audience’s interest in posted content and influence social media algorithms, which can expand a brand’s reach.
The engagement rate, a common metric, measures the number of engagements (reactions, comments, and shares) content receives as a percentage of the audience.
This metric can be calculated in various ways, including dividing the total number of engagements by the number of followers and multiplying by 100 to get a percentage.
In 2024, multi-channel attribution has become a significant trend in marketing, particularly for B2B marketers.
This complex approach involves attributing credit to various marketing touchpoints across different channels that contribute to conversions and drive sales.
B2B marketing often involves numerous touchpoints over a range of channels, making multi-channel attribution crucial for understanding the impact of each touchpoint on the customer journey.
By effectively analyzing this data, marketers can identify which channels are most effective at driving sales and strategically allocate resources and efforts to optimize their marketing campaigns.
For more insights into this, check out this video by The SMB Hub:
8 Important Marketing Metrics Explained
Applying a marketing measurement framework effectively is essential for understanding and enhancing the performance of marketing strategies.
Let’s explore how to implement this framework, incorporating various types of marketing measurement and utilizing marketing metrics formulas:
A marketing measurement plan is a strategic document that defines the data inputs necessary for insightful and accurate reporting.
This plan is guided by business goals and includes first-party data measurements and technical considerations for data availability.
It outlines what needs to be measured but does not specify how success should be quantified. This approach ensures that the necessary components are in place to gauge the success of marketing efforts.
Implementing a marketing measurement plan involves establishing data pipelines and reporting structures.
It requires collaboration with data and analytics stakeholders to map out clear requirements for supporting reporting needs.
This process fosters cross-functional alignment and ensures all stakeholders work towards shared objectives and KPIs.
Building accurate and useful data pipelines is crucial. This involves identifying key data sources, understanding how they connect, and ensuring they collect the right data.
Emphasis should be placed on collecting first-party data to meet evolving user expectations and privacy concerns.
Deciding where and how to collect data is key to creating a robust marketing measurement strategy.
Understanding how users arrive at your domain is vital.
A marketing measurement strategy should consider various traffic sources like direct, organic, display ads, social media, paid ads, email, referrals, and affiliate links.
This helps in understanding user behavior and adjusting efforts in channels accordingly.
It is important to track different user behaviors and align them with funnel stages within the marketing funnel.
This approach provides insights into where users are in their customer journey and helps optimize channels and content.
It involves tracking various types of events, actions, or conversions aligned with different traffic sources and landing pages.
The final element of a marketing measurement plan involves technical considerations for implementing data needs.
This includes choosing the primary analytics solution, dashboarding tools, and tag management systems.
Software tools are essential for managing data, creating reports, and tracking events effectively.
Collaboration between marketing and data teams is crucial to ensure the technical aspects of the plan are implemented correctly.
In this day of tightened budgets and intensified competition, selecting the right metrics and leveraging the insights they provide is more crucial than ever.
It’s not just about gathering data but about distilling it into actionable insights that propel a business forward.
By applying a thoughtful marketing measurement framework, businesses can ensure that every marketing dollar is spent wisely, every strategy is aligned with the brand’s objectives, and every campaign is fine-tuned for optimal performance.
Remember, the key to successful marketing is understanding and applying the right metrics.
Marketing measurement is crucial because it provides a clearer understanding of the effectiveness of your marketing efforts. It helps businesses track the impact of their marketing activities and campaigns, allowing them to see where and how their marketing drives meaningful actions that support their objectives. It also helps identify areas that may not work optimally, enabling adjustments for better ROI. Read the full article to learn why marketing measurement is essential and how to implement it effectively. To gauge the effectiveness of your marketing strategies, it's essential to track critical metrics like cost per lead (CPL), cost per acquisition (CPA), click-through rate (CTR), customer lifetime value (LTV), length of engagement, bounce rate, goal completions, conversion rate by channel, quality of inbound links, and social media engagement. Each of these metrics provides valuable insights into different aspects of your marketing performance. To understand these metrics and how they can benefit your marketing efforts, dive into the full article. Applying marketing measurement effectively involves several steps, including developing a measurement plan, implementing data pipelines and reporting, considering technical requirements and data collection, analyzing traffic sources, tracking user behavior, and planning implementation. These steps help businesses create a robust marketing measurement framework that aligns with their objectives and ensures budgets are spent wisely. Read the full article to get a comprehensive understanding of how to apply marketing measurement.Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of marketing measurement?
What are the essential marketing metrics to track?
How can I apply marketing measurement effectively?
LinkedIn: How can you use zero-based budgeting to optimize your B2B marketing strategy?
Business Insider: Recession will hit the US in 2024 – so get ready for massive interest-rate cuts, UBS says
Forbs: KPIs: What Are They, And Why Are They Important?
Spin Sucks: The Importance of Data Accessibility In Marketing
Salespanel: Revolution Begins: 9 Marketing Analytics Trends for 2023
Daasity: Cost Per Acquisition (CPA) Guide
AdLine: How To Calculate Cost Per Lead (CPL)
Rank Tracker: Why Link Building Is Still Crucial for SEO in 2023
Indeed: Cost Per Acquisition Formula: How To Calculate CPA
Thought leadership, marketing: Clickthrough Rates (CTRs) by Industry: 2024 Report
Daasity: Customer Lifetime Value: The Authoritative Guide [Updated for 2023]
Daasity: Gross Margin: The Authoritative Guide [2023]
HubSpot: 16 Website Metrics to Track for Growth in 2023 and Beyond